STI BASICS

The reality is this – anyone who is sexually active and has unprotected sex can contract a sexually transmitted infection (STI). AHF wants to put an end to the misinformation, stigma, and confusion surrounding STIs.
At AHF Wellness Centers, we offer testing, diagnosis, and if needed, treatment for STIs, free of charge. We also provide valuable information about STIs, safer sex, and when necessary, referrals to medical specialists for further treatment and care.
No appointment is needed.
Our testing counselors can see you on a walk-in basis. You can get fast, free, confidential, and accurate testing at your convenience.
For most STIs, we have rapid tests that can provide same-day results. Depending on the clinic and the availability of specific tests, a client may be able to walk into a clinic and receive a diagnosis in about 30 minutes.
In some clinics and for certain STIs, a rapid test might not be available. In such instances, our care providers will use a “syndromic” approach to help the client. The client will be treated for the symptoms they are experiencing, and test samples will be collected for an in-depth lab analysis. These results will inform the best course of treatment and determine if there is a need for future follow-up visits or procedures.
Everyone diagnosed with an STI is encouraged to inform their sexual partner(s) and invite them to get tested. Our counselors are trained to support clients with partner disclosure and contact follow-up. Every sexually active person has the power to protect those around them from STIs, and we can help make this process less stressful.
While humans are considered sexual beings by nature, abstinence is the most effective way to avoid exposure to an STI.
Condoms have been proven to be effective at preventing the spread of HIV, chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, and unplanned pregnancy via sexual intercourse. Condoms can also reduce the risk of acquiring or spreading the human papillomavirus infection (HPV). Condoms cannot protect from HPV warts that appear on uncovered areas of the genitals or mouth, but the risk of transmission from these areas can be reduced by covering them and keeping the sexual partner out of contact with them. Vaccines are available to prevent HPV strains commonly associated with genital warts and cervical and penis cancers.
In addition to using condoms, a person can reduce their risk of acquiring an STI by limiting the number of sexual partners, having open and honest discussions about each person’s STI status and sexual history, and getting tested regularly.
While many STIs are fairly common, and the first symptoms may be mild or not be present entirely, the consequences of leaving STIs untreated can threaten your health
in many ways. Chlamydia and gonorrhea can lead to epididymitis – an inflammation of the tube connected to the testicles – or pelvic inflammatory disease in women, which affects the uterus and fallopian tubes. Either can be painful and cause infertility. Gonorrhea can also lead to ulcers in the throat or rectum. Syphilis, gonorrhea, and chlamydia can be passed to a child during pregnancy or birth. And having another STI can put a person at greater risk of acquiring HIV.
With a correct course of treatment using antibiotics – gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis are curable. Regular testing, depending on personal risk level, allows a person to get proper treatment and avoid any long-term health consequences.
Get tested regularly and encourage your partners to do the same.
Reasons You Should Care About Testing for STIs:
- There are more than 20 STIs
- STIs are on the rise around the world
- A person may have an undiagnosed STI and unintentionally pass it to a partner
- STIs can negatively impact a person’s future health
- Many STIs can have no symptoms after transmission
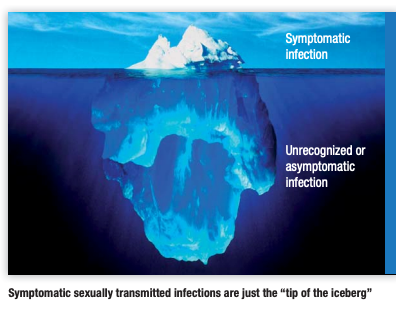 Source: WHO Report on Reproductive Health (PDF)
Source: WHO Report on Reproductive Health (PDF)
Chlamydia is a bacterial infection that can be transmitted from mother to child during birth and among sexually active people.
During unprotected sex, chlamydia can be transmitted through vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone who has it. Chlamydia can be transmitted even if a sex partner does not ejaculate. People with chlamydia may have no symptoms or only mild ones.
People can unknowingly transmit chlamydia even when there are no symptoms. Women are more likely to experience no readily apparent symptoms during a chlamydia infection.
The good news is chlamydia is treatable!
To treat chlamydia, a medical professional will prescribe antibiotics to stop the infection, which can also decrease the chances of having complications later.
Common Symptoms: Many people with a chlamydia infection might not develop any symptoms, which is why getting tested is important. If there are symptoms, they may include the following:
- Pain or burning while urinating
- Unusual discharge (milky, watery, yellowish, strong-smelling) from the penis or vagina
- Swelling of the anus or testicles
- Vaginal bleeding between periods
- Pain during vaginal sex
- Lower abdominal pain
- Infertility and/or pelvic inflammatory disease, as complications
Gonorrhea (sometimes called “the clap” or “the drip”) is a bacterial infection of the penis, urethra, anus, throat, cervix, or vagina. It’s similar to chlamydia in that it infects specific parts of the body and may not have symptoms. Women are more likely to experience no readily apparent symptoms during a gonorrhea infection.
Gonorrhea spreads through anal, oral, or vaginal sex. Semen doesn’t need to be present to transmit gonorrhea, so oral sex without a condom is risky, even if ejaculation happens outside the mouth. If a person performs oral sex on someone who has gonorrhea, that person can develop an infection in their throat.
Due to its prevalence, gonorrhea is gradually becoming resistant to most antibiotics prescribed to treat it. Antimicrobial-resistant gonorrhea refers to a particular strain of bacteria that is immune to the effects of medicine. In most countries with documented cases of antimicrobial-resistant gonorrhea, the most effective treatment requires a single-dose injection of antibiotics. So, it still is treatable!
Untreated gonorrhea can cause serious and permanent health problems. Make sure to get tested if you have any symptoms consistent with gonorrhea or have had unprotected sex.
Common Symptoms: Some people with a gonorrhea infection might not develop any symptoms. If there are symptoms, they may include the following:
- Urethral discharge (the most common symptom)
- Frequent urination
- Sharp pain in the lower abdomen
- Burning during urination or ejaculation
- Increased greenish or yellowish discharge from the penis or vagina
- Vaginal bleeding between periods
- Anal discharge or bloody bowel movements
- Itching around the anus
- Possible infertility, ectopic pregnancy, and/or pelvic inflammatory disease, as complications
Syphilis can be transmitted through direct contact with a syphilis sore during vaginal, anal, or oral sex and can be transmitted to an unborn child during pregnancy. It is uncommon to transmit syphilis through kissing. Gay and bisexual men are at high risk of acquiring syphilis.
Since the syphilis lesions are usually painless, they can easily go unnoticed. Having syphilis once does not make a person immune from getting it again. Even after a successful treatment, you can re-acquire syphilis.
Syphilis is a bacterial infection that can cause sores, which typically disappear within one week even without treatment, and rashes in the initial phase of the disease. Once the initial sores disappear, the infection might enter a secondary phase. This phase, if present, can mimic an allergic reaction or viral infection, making a correct diagnosis more challenging. After the symptomatic phases, syphilis can become “latent” (without any apparent symptoms) and can cause serious harm over several years, including organ damage and death, if left untreated.
Common Symptoms:
- Painless ulcers in the genital area and/or around the neck and mouth
- Skin rashes may appear on the body, including on the palms of the hands and feet
Treatment: Penicillin, a type of antibiotic, is the first and best choice of treatment for syphilis. It is a safe, simple, and effective treatment.
EXPERIENCING SYMPTOMS? GET TESTEDHPV is most frequently spread during vaginal or anal sex. It also develops through close skin-to-skin touching during sex. In most cases, HPV goes away on its own within two years without health problems. But when HPV does not go away, it can cause serious complications like genital warts and certain types of cancer. A sexually active person can develop symptoms years after having sex with someone who has the infection. This makes it hard to know when the person was first infected.
Genital warts are more likely to appear and reoccur among people who smoke or have a weakened immune system, especially people living with HIV. There is no cure for HPV, but warts can be medically removed in several ways, including cryotherapy – freezing them off.
Cervical cancer screenings for women are an important and effective way of preventing and treating complications caused by HPV. Women living with HIV are at a particularly high risk for HPV infection and cervical cancer.
HPV Symptoms for Women: Not everyone with an HPV infection will develop symptoms. If there are symptoms, they may include the following:
Common Symptoms: Some people with a gonorrhea infection might not develop any symptoms. If there are symptoms, they may include the following:
- Urethral discharge (the most common symptom)
- Frequent urination
- Sharp pain in the lower abdomen
- Burning during urination or ejaculation
- Increased greenish or yellowish discharge from the penis or vagina
- Vaginal bleeding between periods
- Anal discharge or bloody bowel movements
- Itching around the anus
- Possible infertility, ectopic pregnancy, and/or pelvic inflammatory disease, as complications
Find a Testing Center or Testing Van near You
Take Control of Your Health. Get HIV and STI Testing at an AHF Wellness Center near You.
GET TESTED TODAYLearn more about HIV symptoms, and check out our HIV test FAQs. Visit our Wellness Clinic for comprehensive STI services. To access our free HIV services and to get tested: Find a clinic. To learn more about HIV in Rwanda visit the UNAIDS Brief on Rwanda.